Last Updated on 08/26/2025 by qhbake
Have you ever noticed that professional biscuit production lines are essentially the backbone behind almost all biscuits available today—whether they are well-known branded products in markets or specialty offerings from personal workshops? The popularity of these production lines has been on a steady rise: large-scale food manufacturers rely on them to achieve mass production, while fledgling food entrepreneurs can also build small-scale production lines with their support. Undoubtedly, they have become an “indispensable piece of equipment” in food processing.
1. Raw Material and Auxiliary Material Pretreatment
At the forefront of the production line lies the raw material and auxiliary material pretreatment stage, where specialized machines operate with high efficiency to ensure material quality:
– Sieving machines are dedicated to “purifying” wheat flour by removing agglomerates and small impurities, guaranteeing the flour’s fineness and preventing any negative impact on the final biscuit texture.
– Grinding machines grind granulated sugar into finer powdered sugar, enabling more uniform blending with other raw materials in subsequent steps.
– Additionally, oil filtration machines and egg cleaning and disinfection machines are employed to ensure every ingredient enters the production process in the cleanest and most suitable state, thus controlling hygiene from the source.
2. Dough Preparation
The core step of dough preparation revolves around professional mixers—equipment far more advanced than household egg beaters, as it can precisely control both mixing intensity and duration:
1. First, it mixes sugar, oil, and eggs into a smooth emulsion.
2. Then, it incorporates wheat flour, leavening agents, and other raw materials.
3. The mixing duration is adjusted according to the type of biscuit: for shortbread biscuits, mixing time is minimized to avoid gluten formation; for tough biscuits, mixing time is extended to enhance the dough’s elasticity. No manual supervision is required throughout this process.
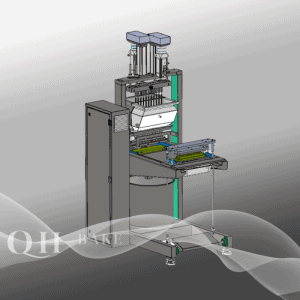
3. Rolling and Molding
The rolling and molding stage is particularly notable, relying on the “golden combination” of rolling machines and molding machines:
– Rolling machines function like fully automated “giant rolling pins.” After passing through several sets of rollers, the dough is pressed into uniform-thickness sheets.
– Molding machines are even more versatile: equipped with various molds, they can produce biscuit blanks in shapes such as teddy bears, flowers, and letters, ensuring neat and consistent results.
– For soda biscuits, a dedicated hole-punching machine is used to create small holes in the blanks, preventing them from puffing up and deforming during baking.
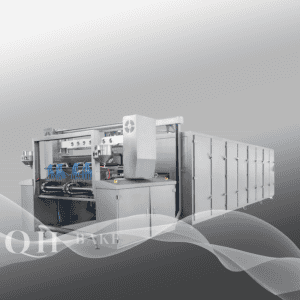
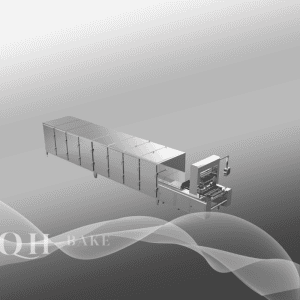
4. Baking
The primary equipment for baking is either a tunnel oven or a hot-air circulation oven, both of which allow for precise temperature and time settings:
– Thin and crispy biscuits are baked at 180–220°C for 8–12 minutes to quickly lock in their crispness.
– Thicker tough biscuits are baked at a lower temperature of 150–180°C for 15–25 minutes to ensure they are fully cooked both inside and out.
During baking, the entire workshop is filled with the aroma of wheat, and watching the soft biscuit blanks turn golden and crispy is a highly satisfying process.
5. Cooling and Finishing
After baking, the biscuits proceed to the cooling and finishing stage:
– Cooling conveyors rapidly lower the temperature of the biscuits. Without rapid cooling, the freshly baked biscuits would be too hot and prone to softening; cooling ensures they maintain a crispy texture.
– Finishing machines sort out biscuits with irregular edges and separate any stuck-together pieces, ensuring each biscuit is neat and uniform—eliminating the need for manual sorting.
6. Packaging
The final packaging stage is handled by high-efficiency packaging machines, which offer strong versatility:
– They can handle various packaging formats, including individual sachets, family-sized packs, and gift boxes, with tight seals to prevent moisture absorption.
– Moreover, the packaging process includes a metal detector to identify and remove any potential small impurities, ensuring the safety of every biscuit that reaches consumers.
Advantages of Professional Biscuit Production Lines
The advantages of such a complete biscuit production line are evident:
1. Clear Division of Labor: Each machine is dedicated to its specific task, eliminating the need for manual switching between operations and significantly improving efficiency compared to manual production.
2. High Stability: Whether producing 100 units or 100,000 units, the texture and shape of the biscuits remain consistent—avoiding the inconsistency often seen in manual production.
3. Strong Flexibility: By replacing molds or adjusting parameters, the line can switch from producing chocolate biscuits to soda biscuits seamlessly, making it suitable for both large-scale mass production and small-batch trial runs.
-
150 Auto starch less gummy candy depositing line: 60,000 gummies/h 280pcs of mold inside machine 8-10PH Cooling unit
-
20S Servo-Form candy depositing Equipment: Cavity PCS: ±20; 100x80x160 Size(cm)
-
300 Auto starch less gummy candy depositing line 120,000 gummies/h 8-10PH Cooling unit 280pcs of twin-mold inside machine
-

50S Servo Control Candy Depositor: Servo; Cavity PCS: ±20; 200x100x170 Size(cm)
-
600 Auto starch less gummy candy depositing line: 240,000 gummies/h 10-20 PH Cooling unit 520pcs of twin-mold inside machine
-
80 Automatic Gummy Candy Production Line: 40,000 gummies/h 5-8PH Cooling unit 200pcs of mold inside machine
-

Automatic Konjac Pearl Making Machine For Sales – Supplier & Manufacuture
-

Automatic Lollipop Production Line For Sale – Candy Machine Factory
-

Automatic Starch-less Depositing Production Line: Revolutionizing Candy Manufacturing